I started by working with plants and plastid genomes during my master’s research. I found the coevolutionary dynamics between nuclear and plastid genomes very interesting during my work with plastome structure variations and plant phylogeny.
After joined nyu, I continued to explore more about host-symbiosis interactions in the context of human & microbes.
Airway host-microbe interactions in lung diseases
The dysbiosis of the lung microbiome plays an important role in lung dieseases pathogenesis. Previous studies found that increased abundance of oral commensal in the lung microbiome affects survival and host gene expressions in lung cancer. This is a collaborative project with Dr. Leopoldo Segal and Dr. Zhang Wang. We are interested in identifying the host-microbiome interactions in lung diseases including lung cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). We have paired metagenomic or metatranscriptomic and host transcriptomic data from lung cancer and COPD cohorts. Topological data analysis network-based co-enrichment analysis was applied to identify the specific microbes co-enriched with genetic driver and risk genes. This work will allow us to systematically identify the potential host-microbe interactions and identify biomarkers.
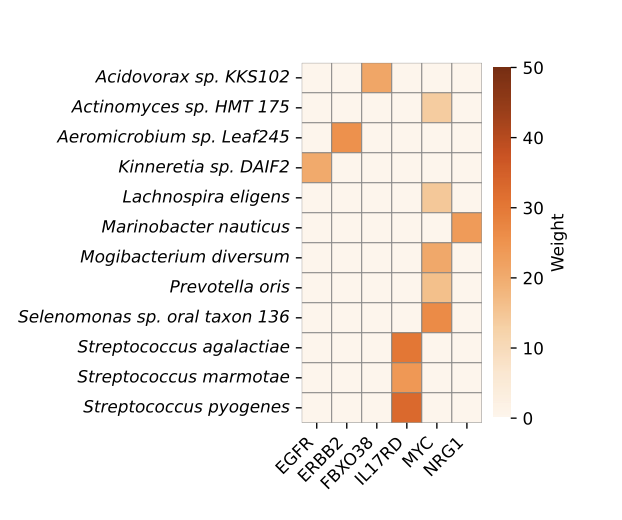
Estimating disease similarity with metagenomic data of the human gut
This work was inspired by the observation that individuals with autism spectrum disorder experience higher chances of gastrointestinal disturbances, such as constipation, diarrhea or abdominal pain. Besides, assessing disease similarity is an essential step preceding disease-based approach for drug repositioning. Our study provides a modest first step in underscoring the potential of integrating microbiome insights into the disease similarity assessment. Recent microbiome research has mainly focused on analyzing individual disease to understand its unique characteristics, which by design excludes comorbidities individuals. We analyzed shotgun metagenomic data from existing studies and identified previously unknown similarities between diseases. Our pipeline represents an initial effort that utilizes both interpretable machine learning and differential abundance analysis to assess microbial similarity between diseases.
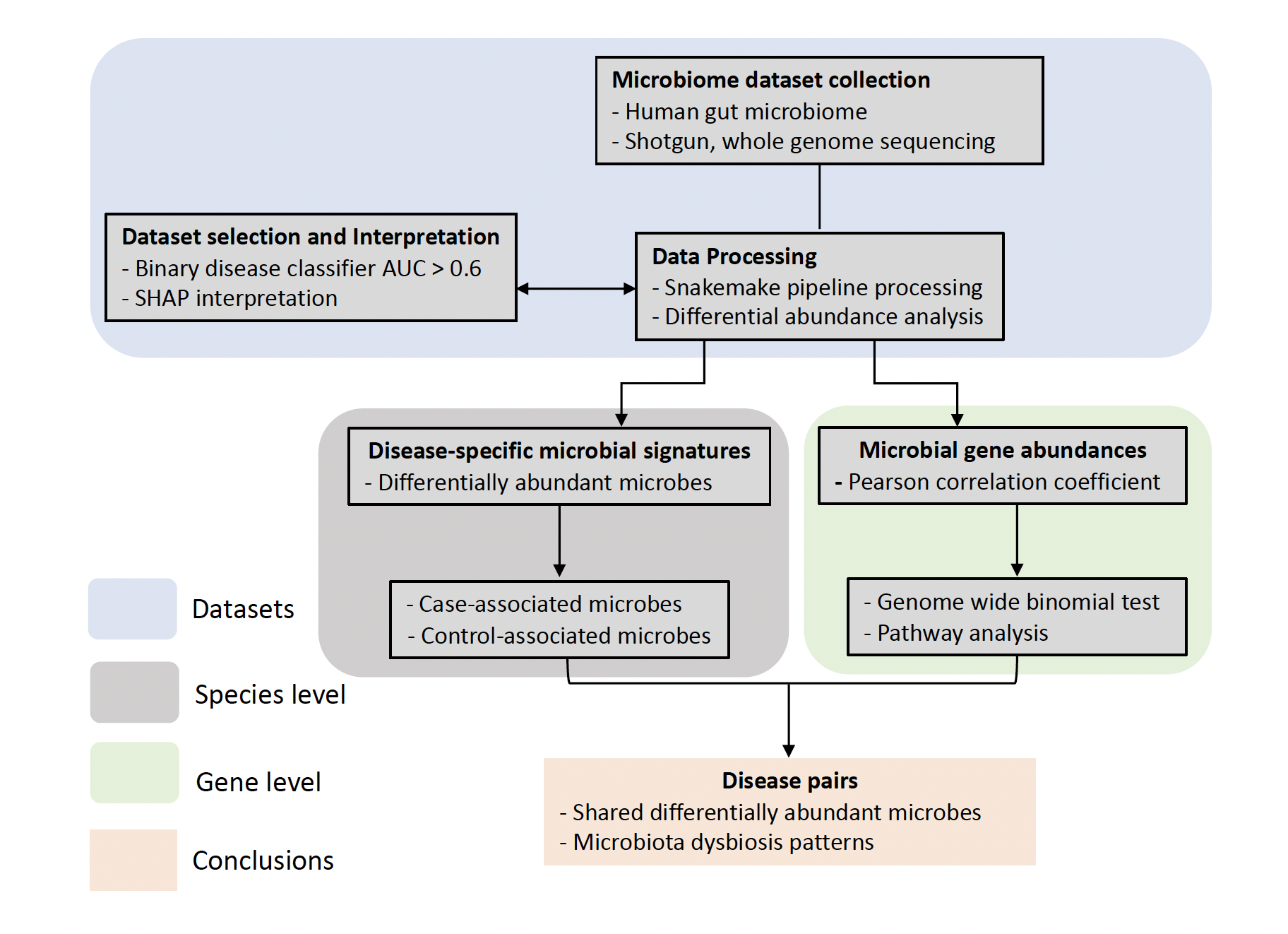
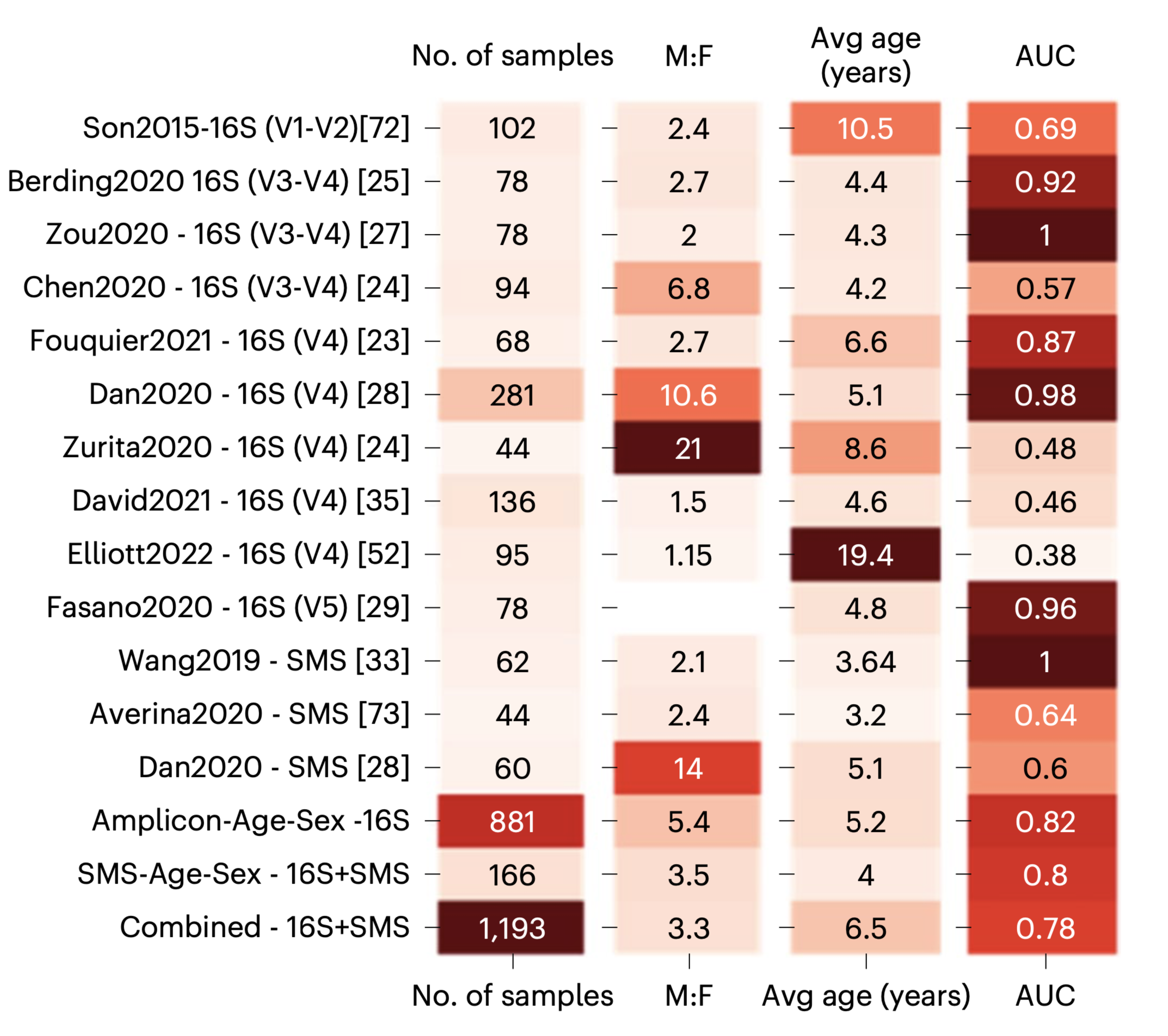
Profiling of the disruption of the gut-brain axis in autism spectrum disorder
Gut microbiome has been considered as the second genome in our body due to its significant impact on our health and well-being. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is heterogeneous neurological condition that has been implicated to be associated with disruptions in the gut-brain axis (GBA) although with limited reproducibility across studies.
I worked with Dr. James Morton, Dr. Gaspar Taroncher-Oldenburg, and Dr. Richard Bonneau on this collaborative project. This study proposed a Bayesian differential ranking algorithm based framework to leverage multi-omic datasets and investigated how the GBA affects ASD. Within this project, I led the data processing for shotgun metagenomics samples and RNA expression data. We found that microbial profiles are predictive of ASD except in the sibling-matched cohorts. I also did co-occurrence analysis to identify candidate viral-microbe interactions. Our results found that Prevotella copri and Bacteroides fragilis both co-occurred with phages enriched in children with ASD or in neurotypical children.
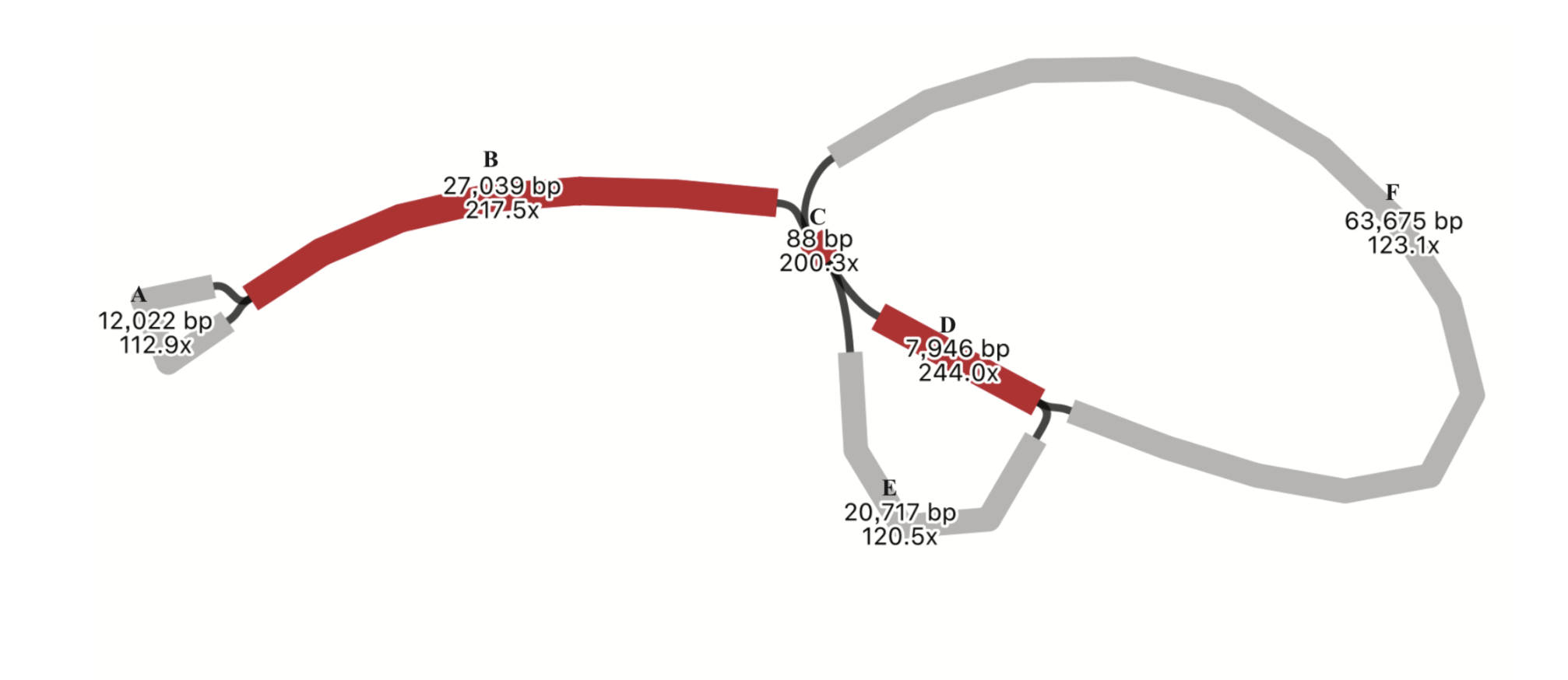
Plastome structure variations of Malpighiales
Plastome plays essential roles in plant biology and functionality. Plastomes of heterotrophic plants are generally highly rearranged, while plastomes of autotrophic angiosperms are relatively conserved. I worked with Dr. Tingshuang Yi and Dr. Jianjun Jin at Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and investigated structural variations of plastomes in autotrophic angiosperm. We used genome skimming data of species from the order Malpighiales. The Malpighiales is a diverse order comprising one of the largest orders of flowering plants. Some examples of well-known species from this order include cassava, willows, passionfruit, mangosteen, and poplars. We found novel plastid genomic rearrangement events in families including Hypericaceae, Podostemaceae,Lophopyxidaceae, Putranjivaceae, Caryocaraceae, and Euphroniaceae.